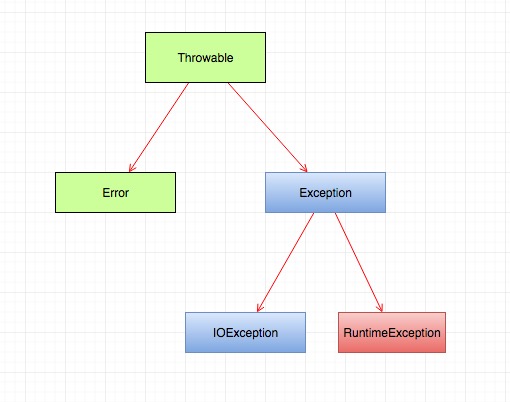
RuntimeException can be simply thrown, all other Exception need to be handled by your code, otherwise compliation won't pass.
Static member/block of a class belongs to the class object itself, it doen't belong to any instance, such member/block is loaded/executed when the classloader decide to load a class. volatile
static variable of class.
This type of member is per Class, and each Class is loaded by a classloader, so if your jvm has multiple class loaders, and they are both loading the same class, then the static member get copied as many as class loader.
Method invocation in Java.
there are several jvm ops to invoke a method in java:
- invokespecial: static binding, instance method(
super,<init>privatemethod) - invokestatic: static binding, class method
- invokevirtual: dynamic binding, all other instance method.
- invokeinterface dynamic binding, instance methods called using a interface reference, such as list.size().
static binding means called based on the reference type, NOT the class of object it refers to. dynamic binding means called based the class type of the real object.
class mantain a method table, instance method(not super, init, private) it can find indirectly using the method table, but if you have interface reference, it first need to find the refered class, then resolved using that class's method table. so it might be slow.